Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemical Engineering /
case-study-polymer-flow-example-3-1-a-polymer-flows-steadily-in-the-horizontal-pipe-of-fig-e3-pa311
(Solved): Case study: Polymer flow (Example 3.1) A polymer flows steadily in the horizontal pipe of Fig. E3. ...
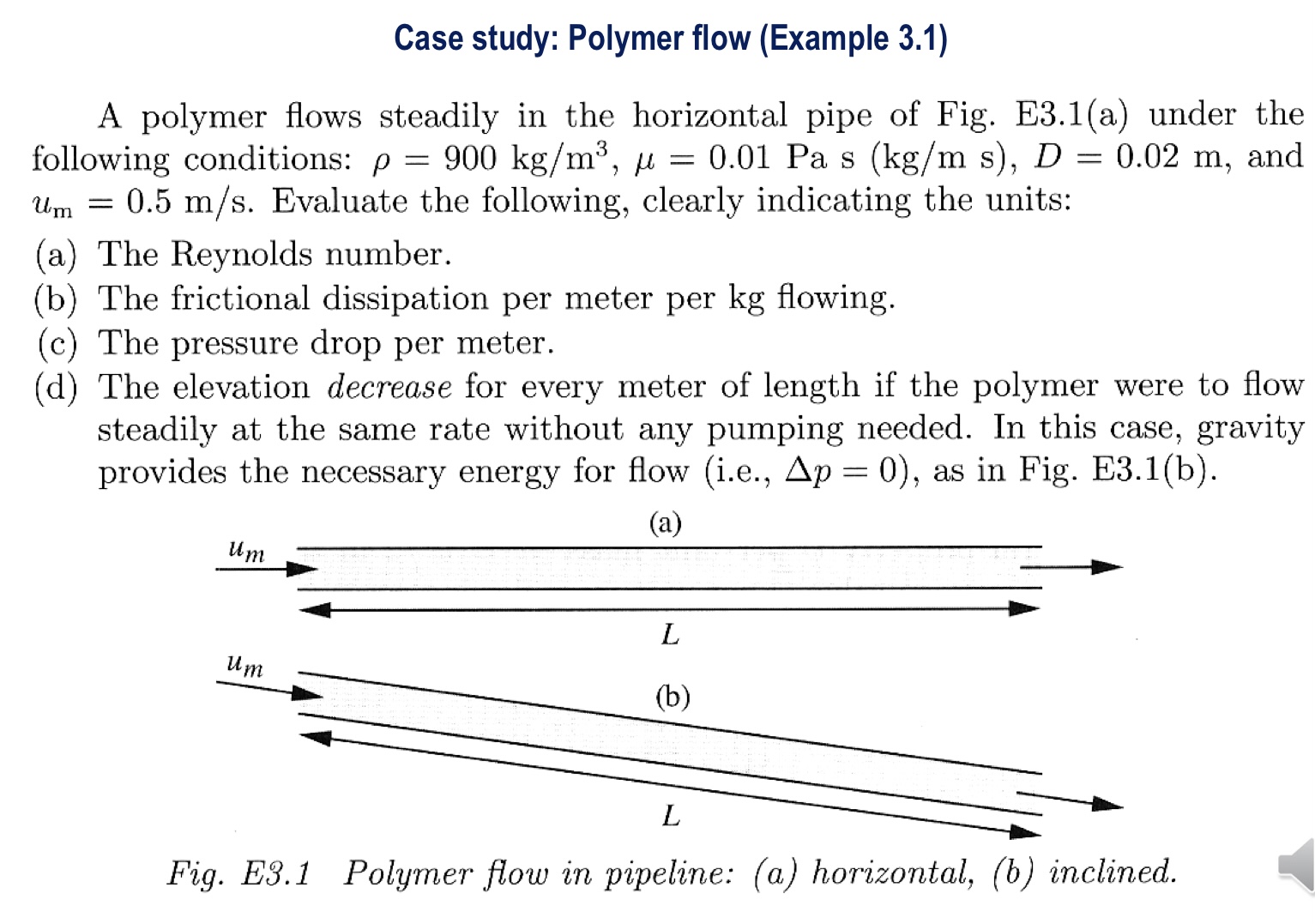
Case study: Polymer flow (Example 3.1) A polymer flows steadily in the horizontal pipe of Fig. E3.1(a) under the following conditions:
\rho =900k(g)/(m^(3)),\mu =0.01Pas(k(g)/(m)s),D=0.02m, and
u_(m)=0.5(m)/(s). Evaluate the following, clearly indicating the units: (a) The Reynolds number. (b) The frictional dissipation per meter per
kgflowing. (c) The pressure drop per meter. (d) The elevation decrease for every meter of length if the polymer were to flow steadily at the same rate without any pumping needed. In this case, gravity provides the necessary energy for flow (i.e.,
\Delta p=0), as in Fig. E3.1(b). (a) Fig. E3.1 Polymer flow in pipeline: (a) horizontal, (b) inclined.