please solve this using C++ language (Advanced data structure) please
Using the stack class from the textbook, implement the span2 function from Lecture 8 Slides.
Using historical data of any stock of your choice, compute the span for each data point.
Find all peaks in the stock price using the span.
***********************Stack Class from textbook********************************************

*******************************************************************************************************************************
******************************Span2 Function*********************************************************************************
 ***************************************************************************************************************************************
***************************************************************************************************************************************
**************************************************Other useful info*******************************************************************

\( \begin{array}{ll}\text { template }\langle\text { typename } \mathrm{E}\rangle & / / \text { an interface for a stack } \\ \text { class Stack \{ } \\ \text { public: } \\ \text { int size() const; } & / / \text { number of items in stack } \\ \text { bool empty() const; } & / / \text { is the stack empty? } \\ \text { const E\& top() const throw(StackEmpty); } & / / \text { the top element } \\ \text { void push(const E\& e); } & / / \text { push } \times \text { onto the stack } \\ \text { void pop() throw(StackEmpty); } & / / \text { remove the top element } \\ \}\end{array} \)
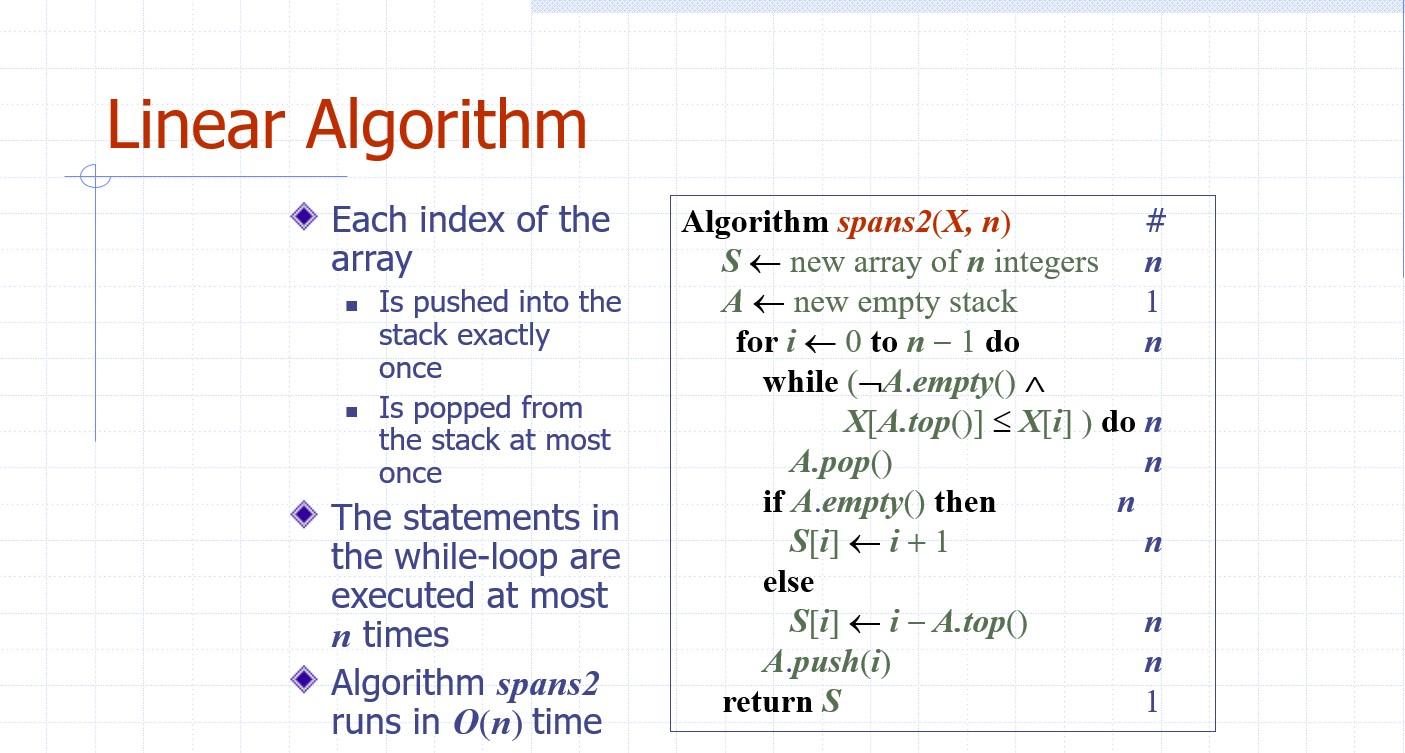
Linear Algorithm
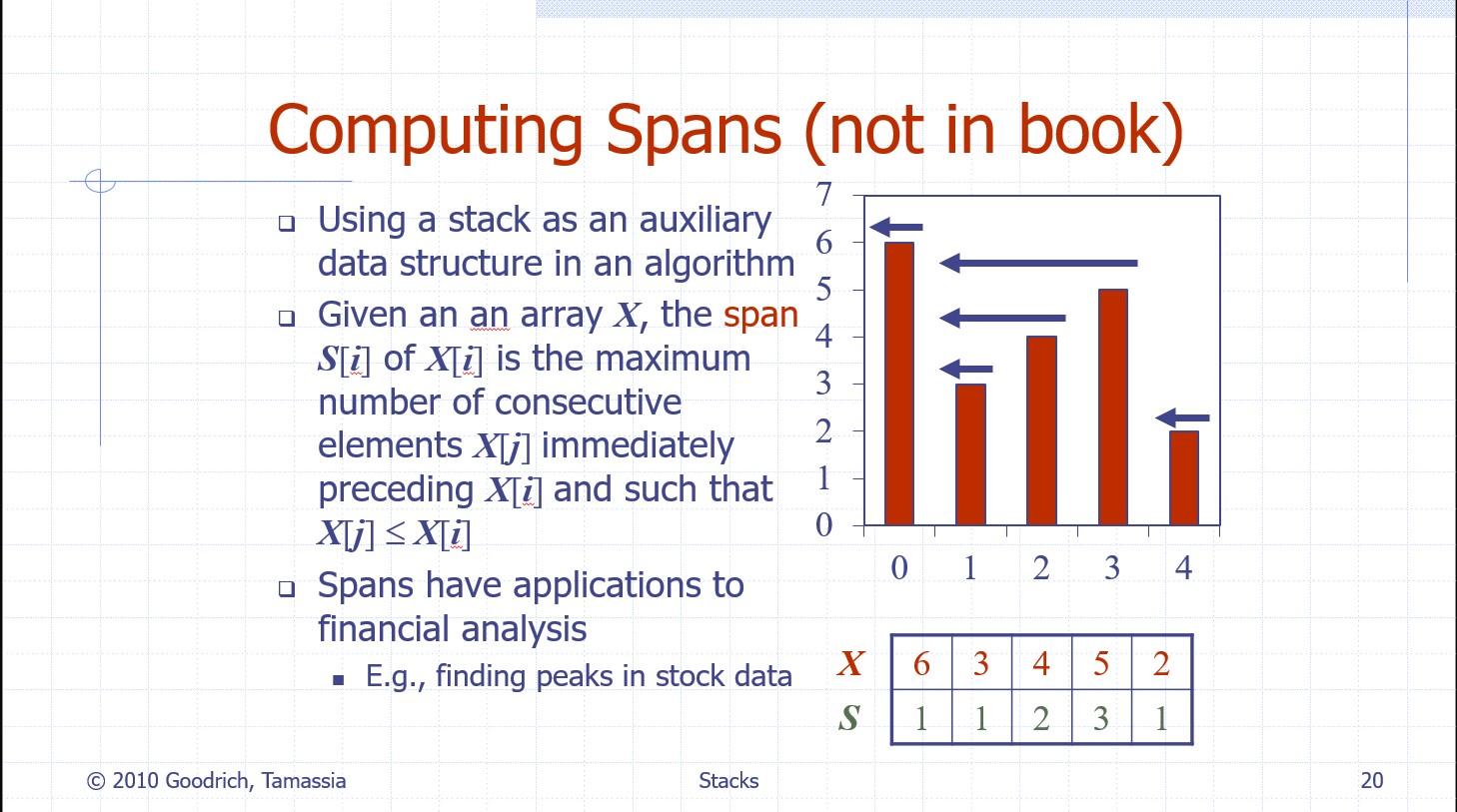
Computing Spans (not in book) - Using a stack as an auxiliary data structure in an algorithm - Given an an array \( \boldsymbol{X} \), the span \( \boldsymbol{S}[\boldsymbol{i}] \) of \( \boldsymbol{X}[\boldsymbol{i}] \) is the maximum number of consecutive elements \( X[j] \) immediately preceding \( \boldsymbol{X}[\boldsymbol{i}] \) and such that \( \boldsymbol{X}[j] \leq \boldsymbol{X}[\boldsymbol{i}] \) Spans have applications to financial analysis - E.g., finding peaks in stock data
Computing Spans with a Stack We keep in a stack the indices of the elements visible when "looking back" - We scan the array from left to right - Let \( i \) be the current index - We pop indices from the stack until we find index \( \boldsymbol{j} \) such that \( \boldsymbol{X}[\boldsymbol{i}]<\boldsymbol{X}[\boldsymbol{j}] \) - We set \( S[i] \leftarrow i-j \) - We push \( \boldsymbol{x} \) onto the stack



