Home /
Expert Answers /
Finance /
37-a-return-to-example-16-1-use-the-binomial-model-to-value-a-one-year-european-put-option-with-pa202
(Solved): 37. a. Return to Example 16.1. Use the binomial model to value a one-year European put option with ...

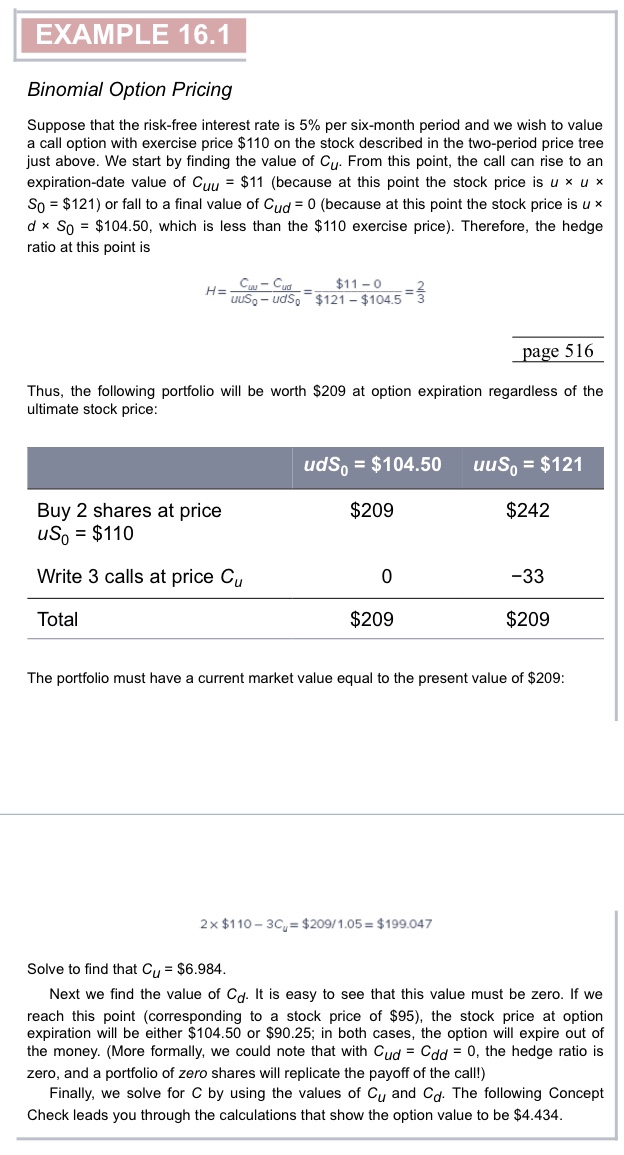
37. a. Return to Example 16.1. Use the binomial model to value a one-year European put option with exercise price on the stock in that example. b. Show that your solution for the put price satisfies put-call parity. (LO 16-2)
B?nomial Opt?on Pr?c?ng Suppose that the risk-free interest rate is per six-month period and we wish to value a call option with exercise price on the stock described in the two-period price tree just above. We start by finding the value of . From this point, the call can rise to an expiration-date value of (because at this point the stock price is ) or fall to a final value of (because at this point the stock price is , which is less than the exercise price). Therefore, the hedge ratio at this point is page 516 Thus, the following portfolio will be worth at option expiration regardless of the ultimate stock price: The portfolio must have a current market value equal to the present value of : Solve to find that . Next we find the value of . It is easy to see that this value must be zero. If we reach this point (corresponding to a stock price of \$95), the stock price at option expiration will be either or ; in both cases, the option will expire out of the money. (More formally, we could note that with , the hedge ratio is zero, and a portfolio of zero shares will replicate the payoff of the call!) Finally, we solve for by using the values of and . The following Concept Check leads you through the calculations that show the option value to be .