Home /
Expert Answers /
Computer Science /
a-vector-contains-both-positive-and-negative-numbers-in-random-order-write-a-function-to-rearrang-pa481
(Solved): A vector contains both positive and negative numbers in random order. Write a function to rearrang ...
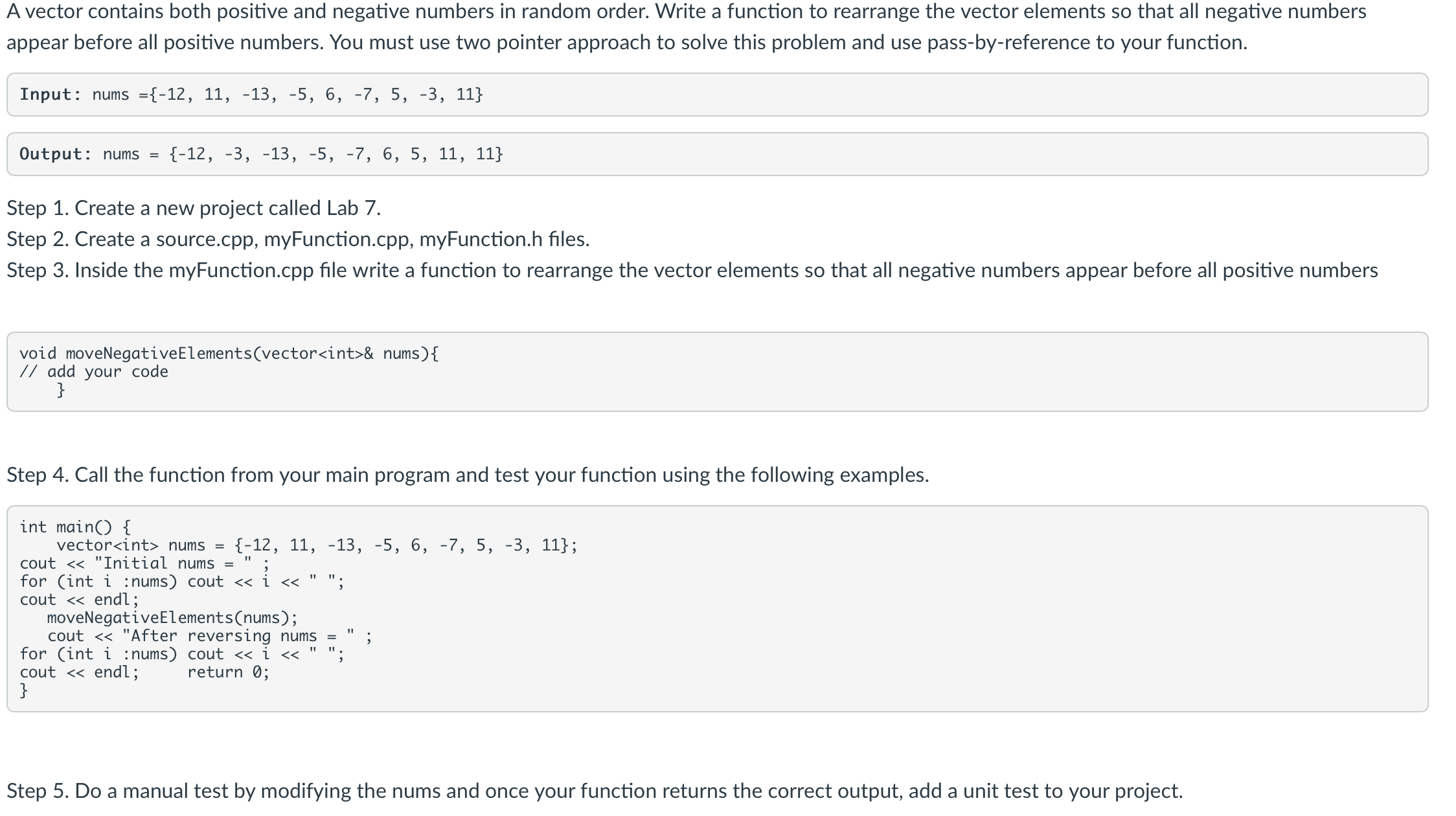
A vector contains both positive and negative numbers in random order. Write a function to rearrange the vector elements so that all negative numbers appear before all positive numbers. You must use two pointer approach to solve this problem and use pass-by-reference to your function. Input: nums Output: nums Step 1. Create a new project called Lab 7. Step 2. Create a source.cpp, myFunction.cpp, myFunction.h files. Step 3. Inside the myFunction.cpp file write a function to rearrange the vector elements so that all negative numbers appear before all positive numbers void moveNegativeElements (vector int nums) \{ // add your code \} void moveNegativeElements (vector int nums) \{ I/ add your code \} Step 4. Call the function from your main program and test your function using the following examples. int main() \{ vector int nums cout "Initial nums for (int ;ums) cout cout endi; moveNegativeElements(nums); cout "After reversing nums for (int i nums) cout cout endi; return \} int vector nums cout "Initial nums ; for (int :nums) cout " cout endl; moveNegativeElements(nums); cout "After reversing nums "; for (int :nums) cout "; cout endl; return ; \}
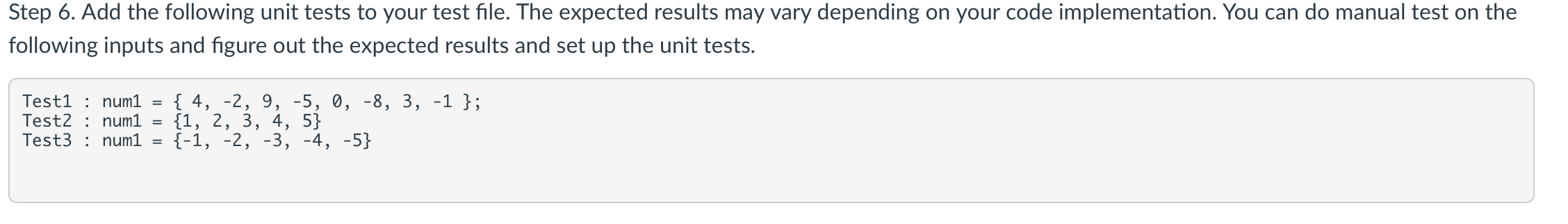
Step 6. Add the following unit tests to your test file. The expected results may vary depending on your code implementation. You can do manual test on the following inputs and figure out the expected results and set up the unit tests.
Expert Answer
The required code for the given scenario :