Home /
Expert Answers /
Biology /
activity-1-1-1-replicate-the-dna-sequence-shown-below-t-a-c-cg-t-t-t-g-a-g-c-g-g-g-c-c-c-a-a-a-g-pa564
(Solved): Activity 1-1 1. Replicate the DNA sequence shown below: T A C CG T T T G A G C G G G C C C A A A G ...
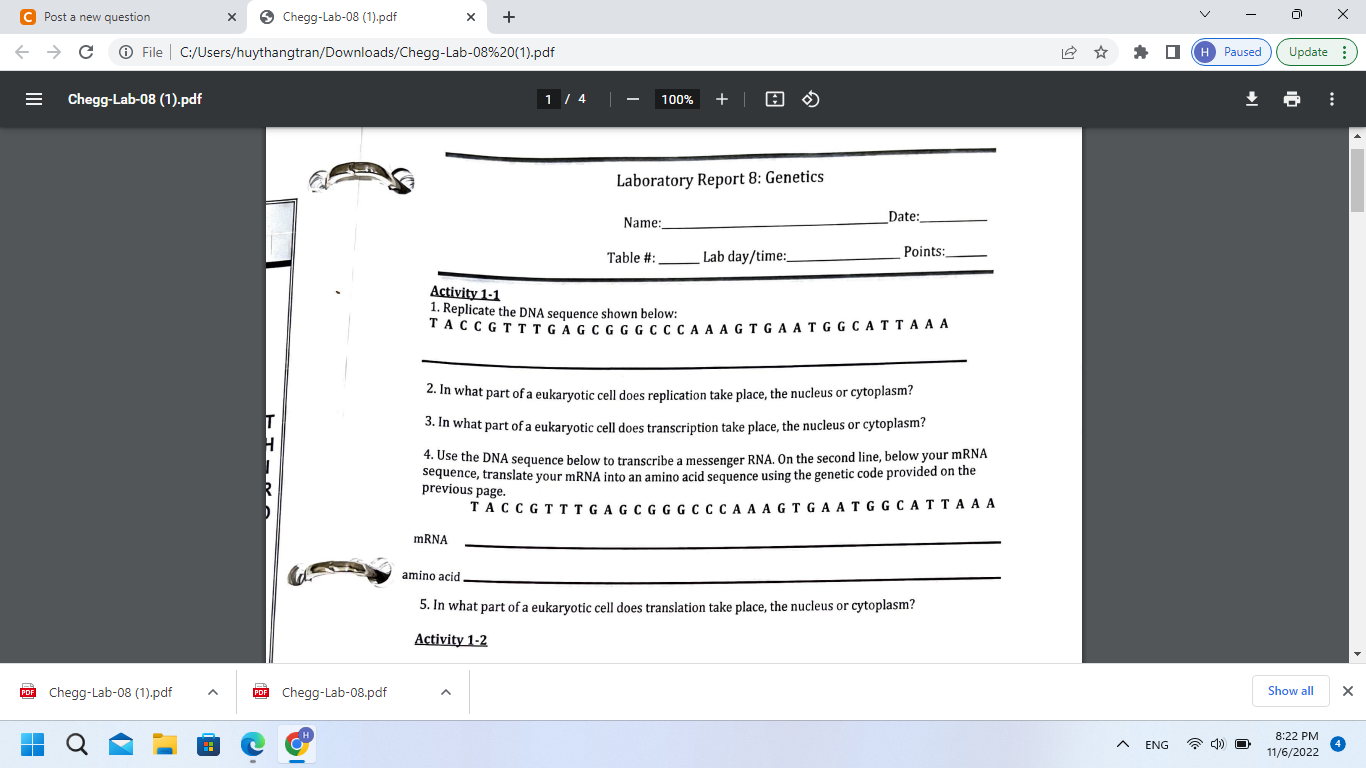
Activity 1-1 1. Replicate the DNA sequence shown below: T A C CG T T T G A G C G G G C C C A A A G T G A A T G G C A T T A A A 2. In what part of a eukaryotic cell does replication take place, the nucleus or cytoplasm? 3. In what part of a eukaryotic cell does transcription take place, the nucleus or cytoplasm? 4. Use the DNA sequence below to transcribe a messenger RNA. On the second line, below your mRNA sequence, translate your mRNA into an amino acid sequence using the genetic code provided on the previous page. T A C C G T T T G A G G G G C C A A A G T GA A T G G C A T T A A A mRNA amino acid 5. In what part of a eukaryotic cell does translation take place, the nucleus or cytoplasm?
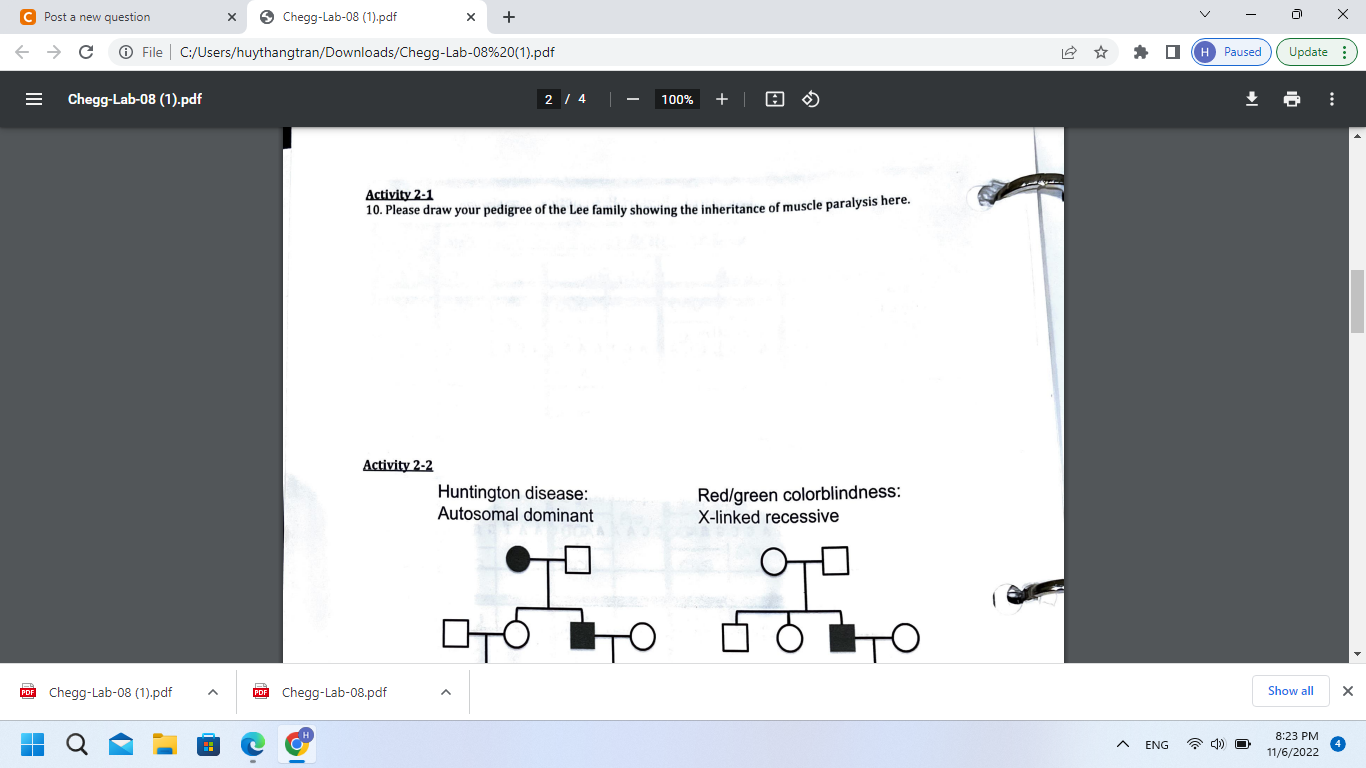
Activity \( 2-1 \) 10. Please draw your pedigree of the Lee family showing the inheritance of muscle paralysis here. Activity 2-2
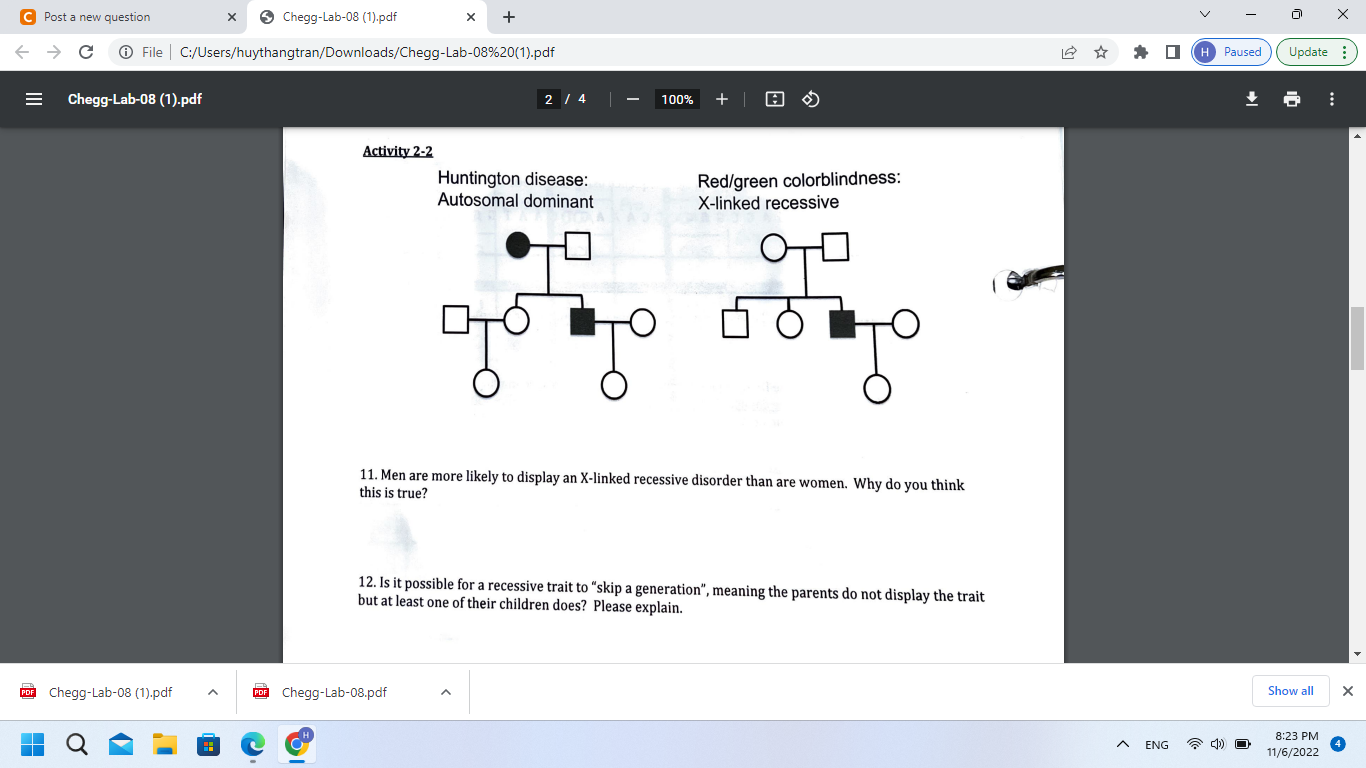
Huntington disease: Red/green colorblindness: Autosomal dominant X-linked recessive 11. Men are more likely to display an X-linked recessive disorder than are women. Why do you think this is true? 12. Is it possible for a recessive trait to "skip a generation", meaning the parents do not display the trait but at least one of their children does? Please explain.
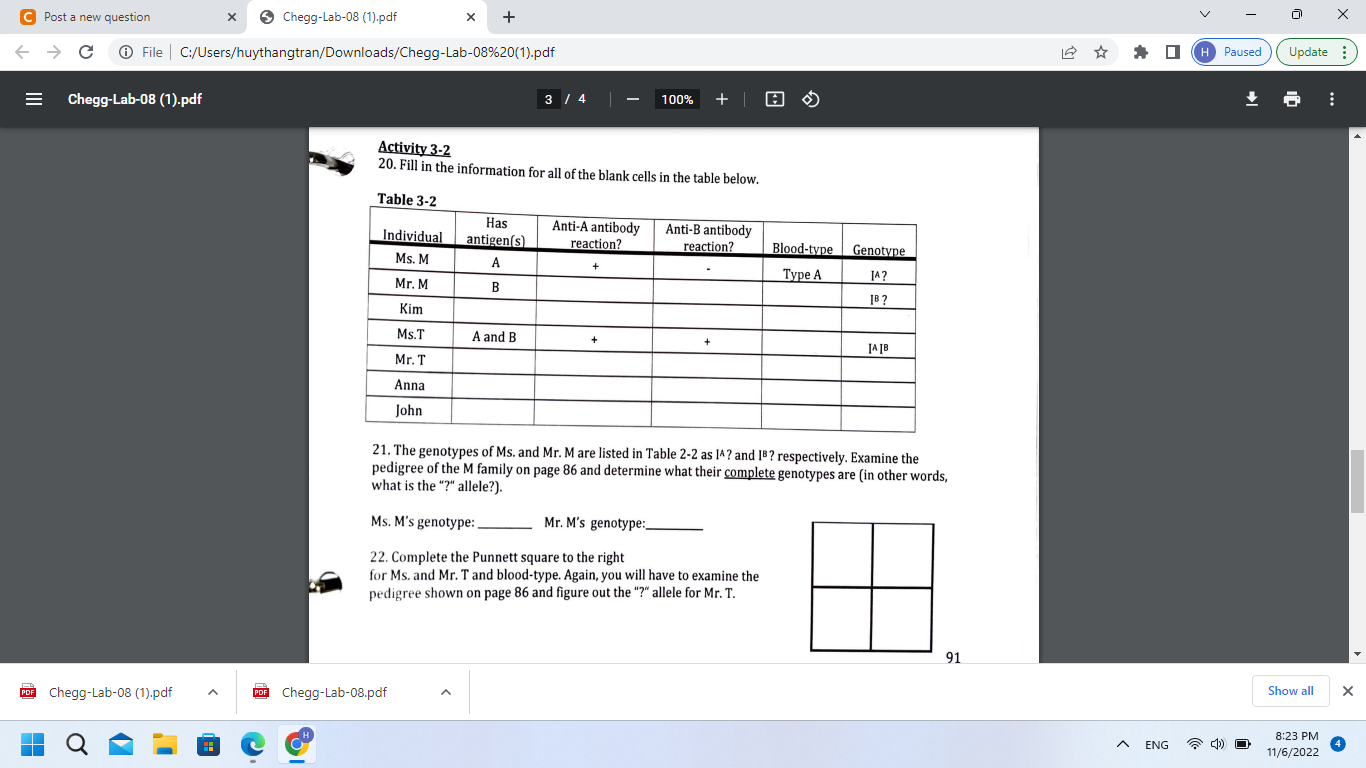
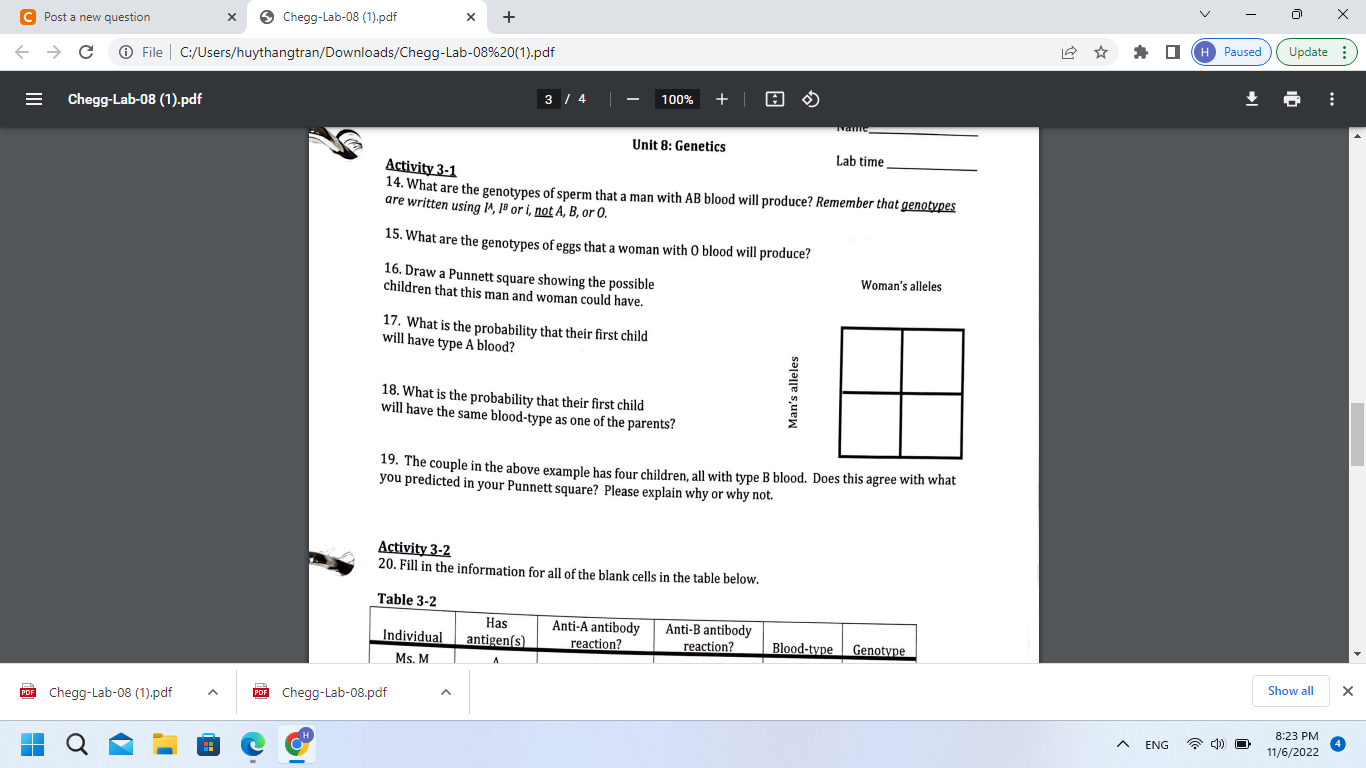
Activity 3-2 20. Fill in the information for all of the blank cells in the table below. Tahla on 21. The genotypes of Ms. and Mr. M are listed in Table 2-2 as IA ? and IB ? respectively. Examine the pedigree of the M family on page 86 and determine what their complete genotypes are (in other words, what is the "?" allele?). Ms. M's genotype: \( \quad \) Mr. M's genotype: 22. Complete the Punnett square to the right for Ms. and Mr. T and blood-type. Again, you will have to examine the pedigree shown on page 86 and figure out the "?" allele for Mr. T.
17. What is the probability that their first child will have type A blood? 18. What is the probability that their first child will have the same blood-type as one of the parents? 19. The couple in the above example has four children, all with type B blood. Does this agree with what you predicted in your Punnett square? Please explain why or why not. Activity 3-2 20. Fill in the information for all of the blank cells in the table below.
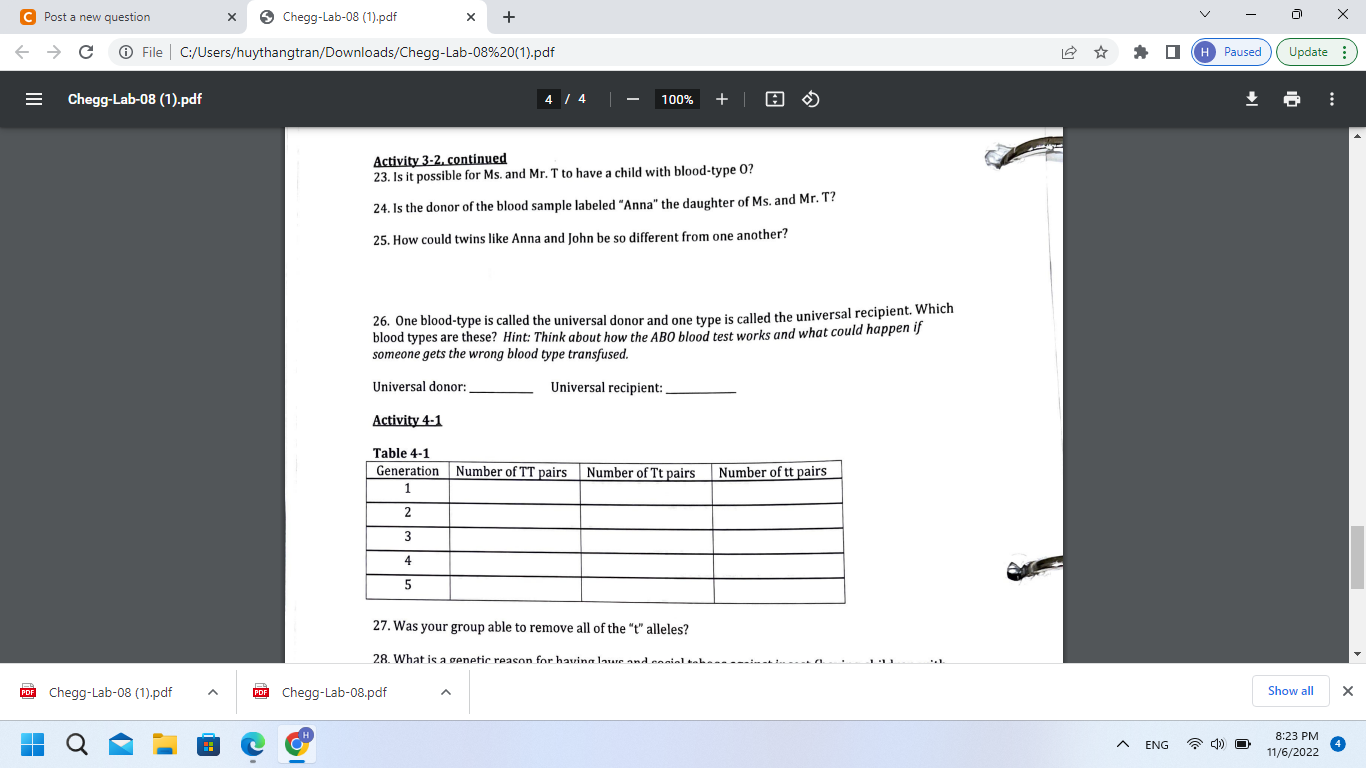
Activity 3-2. continued 23. Is it possible for Ms. and Mr. T to have a child with blood-type 0 ? 24. Is the donor of the blood sample labeled "Anna" the daughter of Ms. and Mr. T? 25. How could twins like Anna and John be so different from one another? 26. One blood-type is called the universal donor and one type is called the universal recipient. Which blood types are these? Hint: Think about how the ABO blood test works and what could happen if someone gets the wrong blood type transfused. Universal donor: Universal recipient: Activity 4-1 27. Was your group able to remove all of the "t" alleles?
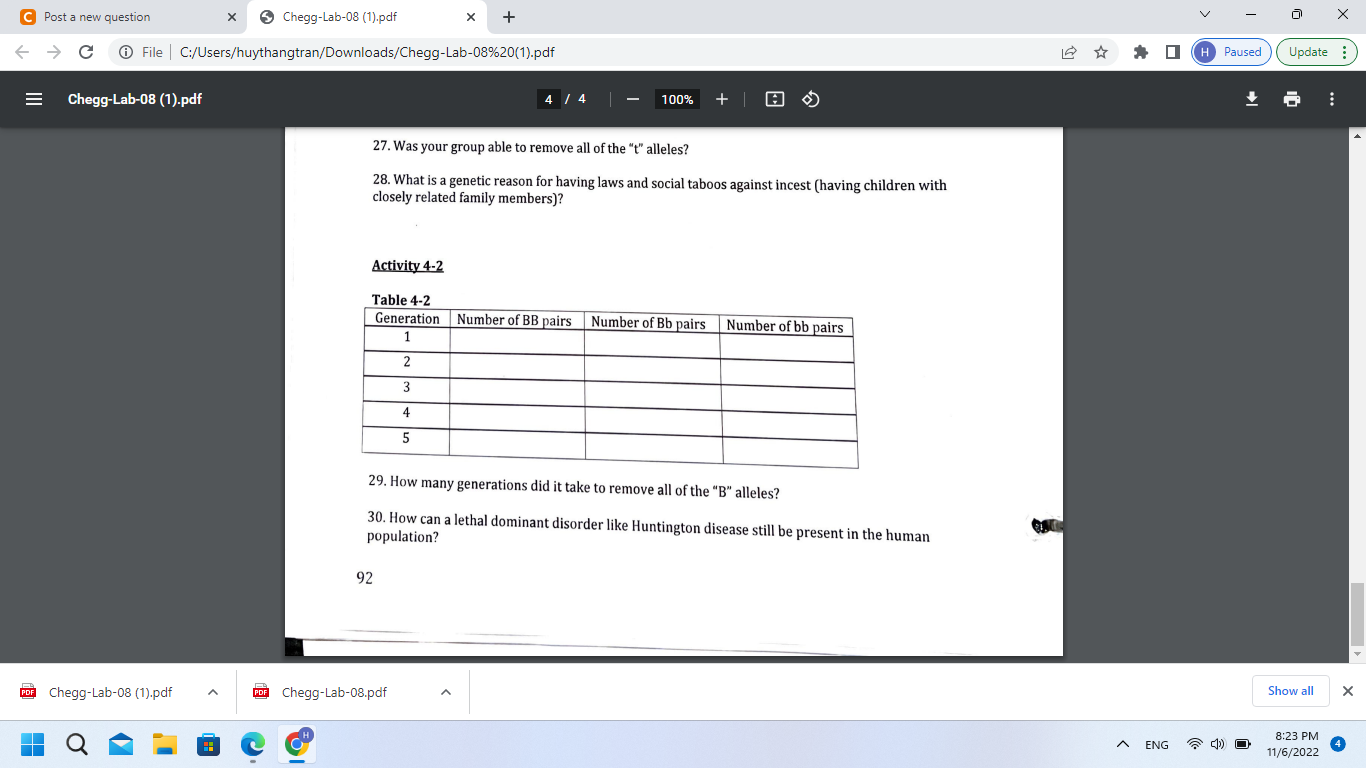
27. Was your group able to remove all of the " \( t \) " alleles? 28. What is a genetic reason for having laws and social taboos against incest (having children with closely related family members)? Activity 4-2 Table 4-2 29. How many generations did it take to remove all of the "B" alleles? 30. How can a lethal dominant disorder like Huntington disease still be present in the human population?