Home /
Expert Answers /
Electrical Engineering /
consider-the-circuit-model-of-the-electrode-skin-interface-below-the-a-g-a-gcl-electrode-has-a-ha-pa686
(Solved): Consider the circuit model of the electrode-skin interface below. The A(g)/(A)gCl electrode has a ha ...
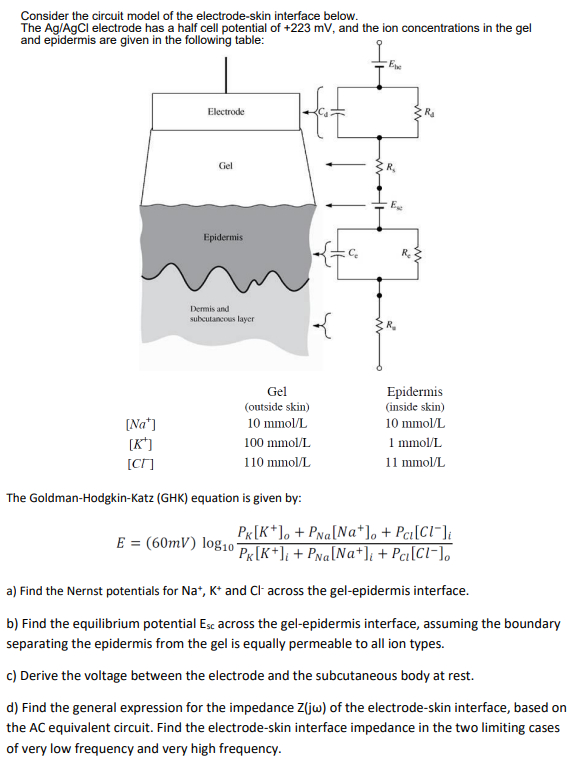
Consider the circuit model of the electrode-skin interface below.
The A(g)/(A)gCl electrode has a half cell potential of +223 mV , and the ion concentrations in the gel
and epidermis are given in the following table:
The Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz (GHK) equation is given by:
E=(60mV)log_(10)((P_(K)[K^(+)]_(o)+P_(Na)[Na^(+)]_(o)+P_(Cl)[Cl^(-)]_(i))/(P_(K)[K^(+)]_(i)+P_(Na)[Na^(+)]_(i)+P_(Cl)[Cl^(-)]_(o)))
aNa^(+),K^(+)and Cl^(-)across the gel-epidermis interface.
bE_(sc) across the gel-epidermis interface, assuming the boundary
separating the epidermis from the gel is equally permeable to all ion types.
cZ(j\omega ) of the electrode-skin interface, based on
the AC equivalent circuit. Find the electrode-skin interface impedance in the two limiting cases
of very low frequency and very high frequency.