(Solved): Consideration : How Can Fragments of DNA Be Separated From One Another? Agarose gel electrophoresis ...
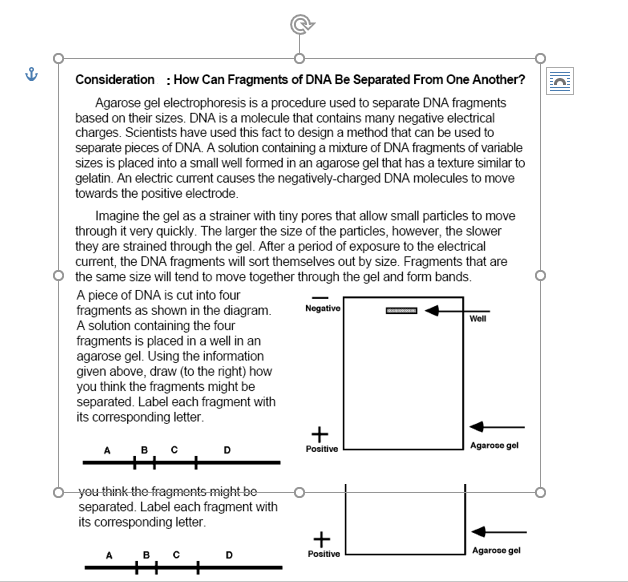
Consideration : How Can Fragments of DNA Be Separated From One Another? Agarose gel electrophoresis is a procedure used to separate DNA fragments based on their sizes. DNA is a molecule that contains many negative electrical charges. Scientists have used this fact to design a method that can be used to separate pieces of DNA. A solution containing a mixture of DNA fragments of variable sizes is placed into a small well formed in an agarose gel that has a texture similar to gelatin. An electric current causes the negatively-charged DNA molecules to move towards the positive electrode. Imagine the gel as a strainer with tiny pores that allow small particles to move through it very quickly. The larger the size of the particles, however, the slower they are strained through the gel. After a period of exposure to the electrical current, the DNA fragments will sort themselves out by size. Fragments that are the same size will tend to move together through the gel and form bands. A piece of DNA is cut into four fragments as shown in the diagram. A solution containing the four fragments is placed in a well in an agarose gel. Using the information given above, draw (to the right) how you think the fragments might be separated. Label each fragment with its corresponding letter. you think the fragments might be separated. Label each fragment with its corresponding letter. A C