Every table has to have one and only one primary key – and each value in the primary key column has to be unique for every row
A table does not have to have a foreign key but can have many foreign keys. The value of a foreign key has to already exists as a primary key in another table. A foreign key’s value can be repeated many times within a table.
The table that gets the foreign key is determined by the maximum cardinalities between two tables. For example in the following:
In the relationship between person and auto, Since Auto has the many next to it, you take the primary key from the person table and put it as a foreign key in the Auto table
In the relationship between auto and state, since the many is next to the auto, you take the primary key from the state table and put it as a foreign key in the auto table.
In the relationship between auto and dealer, there is a many to many maximum relationship. In this situation you need to develop a new table called a relationship table. In a relationship table the primary key is a concatenated or combination primary key. The primary key is the Auto primary key plus the Dealer primary key. The combination of the values of these two keys can not be repeated in a relationship table.
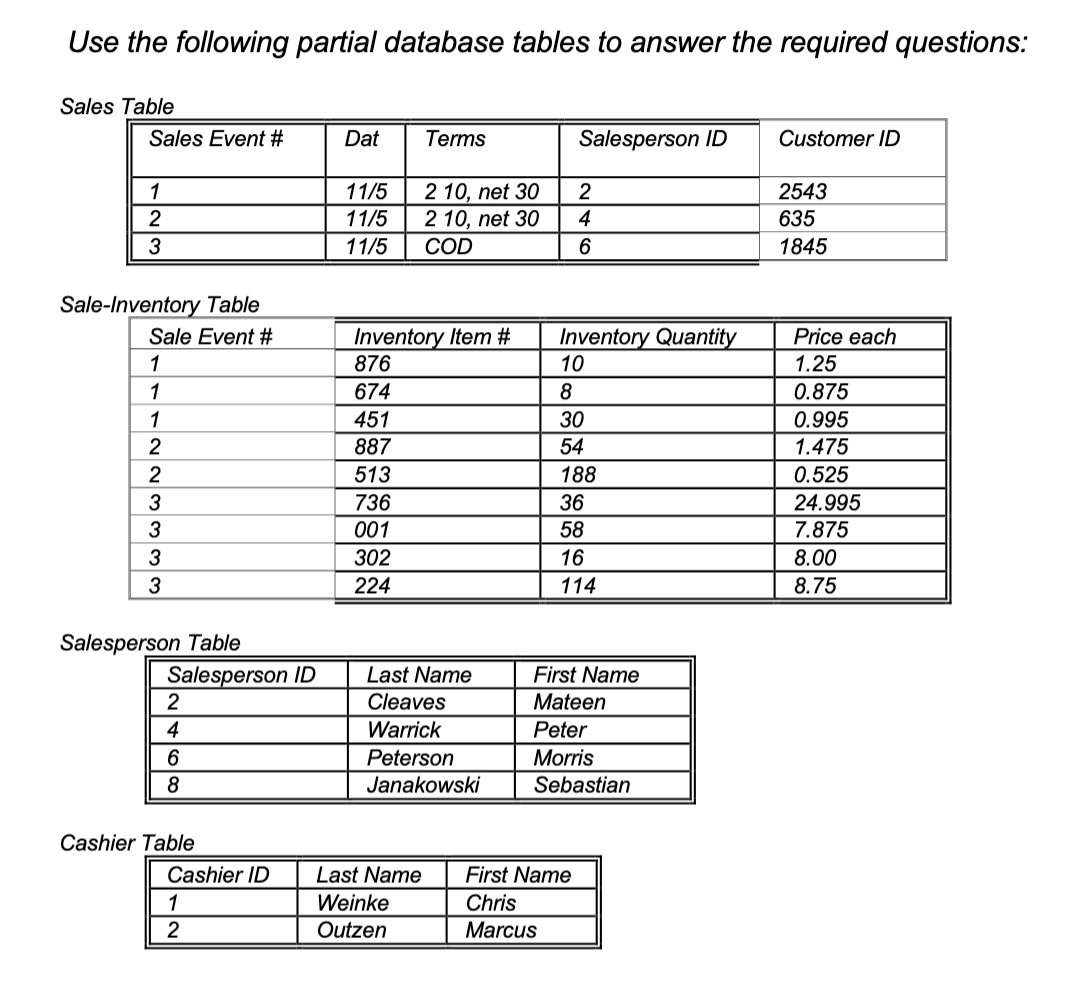
Use the following partial database tables to answer the required questions: Sales Tahlo Sale-Inventan, Tahio Salesperson Table Cashier Table
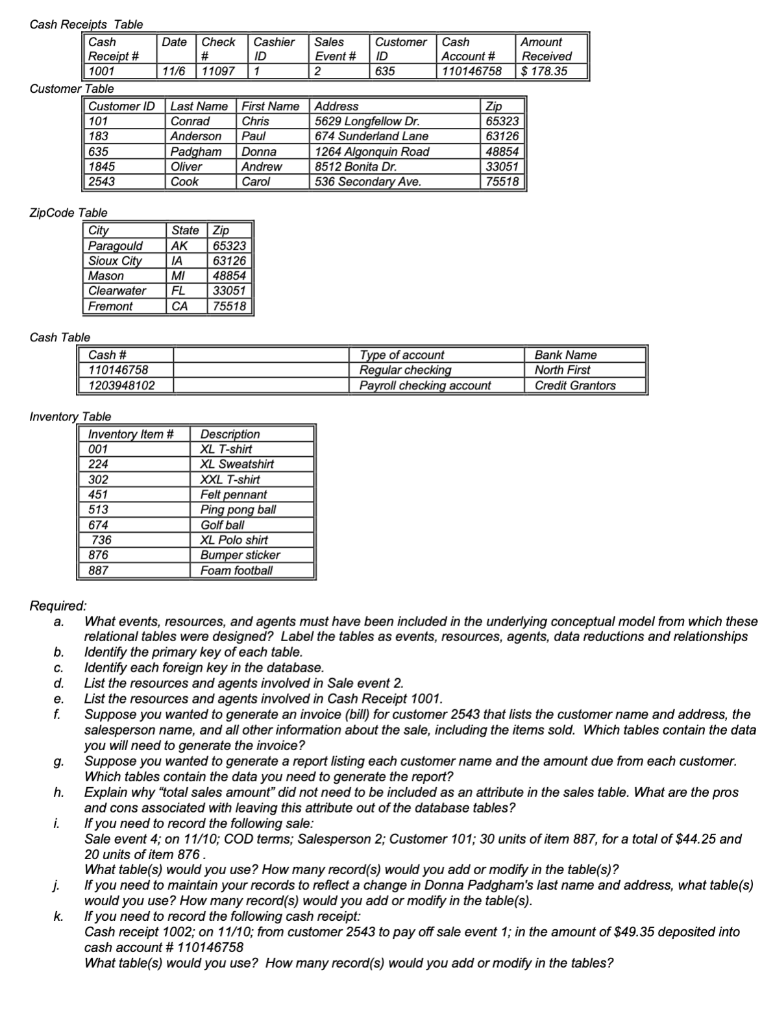
Cash Rerointe Tahlo Customer I anue ZipCode Table Cash Tahla Inventorv Table Required: a. What events, resources, and agents must have been included in the underlying conceptual model from which these relational tables were designed? Label the tables as events, resources, agents, data reductions and relationships b. Identify the primary key of each table. c. Identify each foreign key in the database. d. List the resources and agents involved in Sale event 2. e. List the resources and agents involved in Cash Receipt 1001. f. Suppose you wanted to generate an invoice (bill) for customer 2543 that lists the customer name and address, the salesperson name, and all other information about the sale, including the items sold. Which tables contain the data you will need to generate the invoice? g. Suppose you wanted to generate a report listing each customer name and the amount due from each customer. Which tables contain the data you need to generate the report? h. Explain why "total sales amount" did not need to be included as an attribute in the sales table. What are the pros and cons associated with leaving this attribute out of the database tables? i. If you need to record the following sale: Sale event 4; on 11/10; COD terms; Salesperson 2; Customer 101; 30 units of item 887, for a total of $44.25 and 20 units of item 876. What table(s) would you use? How many record(s) would you add or modify in the table(s)? j. If you need to maintain your records to reflect a change in Donna Padgham's last name and address, what table(s) would you use? How many record(s) would you add or modify in the table(s). k. If you need to record the following cash receipt: Cash receipt 1002; on 11/10; from customer 2543 to pay off sale event 1; in the amount of $49.35 deposited into cash account \# 110146758 What table(s) would you use? How many record(s) would you add or modify in the tables?

