Home /
Expert Answers /
Electrical Engineering /
for-the-mos-differential-pair-with-a-common-mode-voltage-vm-applied-as-shown-in-fig-8-2-let-vdd-pa310
(Solved): For the MOS differential pair with a common-mode voltage VM applied, as shown in Fig. 8.2, let VDD = ...
For the MOS differential pair with a common-mode voltage VM applied, as shown in Fig. 8.2, let VDD = V=1.5 V, k(W/L) = 4 mA/V, V = 0.5 V, I = 0.4 mA, and R, = 2.5 k2, and neglect channel-length modulation. Assume that the current source I requires a minimum voltage of 0.4 V to operate properly. (a) Find Voy and Ves for each transistor. GS (b) For V=0, find Vs In I VDI and V (c) Repeat (b) for VCM +1 V. (d) Repeat (b) for VM=-0.2 V. CM (e) What is the highest permitted value of VM? (f) What is the lowest value allowed for Va? UGI |1? DI O RD VIDI 2? VIDI VDD iD2 V D2 A {R 9? RD OUD2 VG2
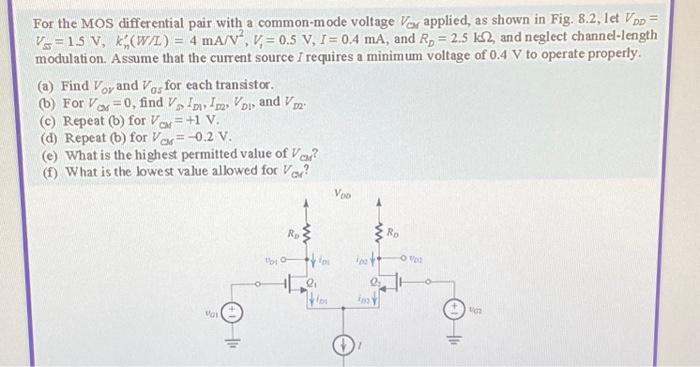
, and , and neglect channel-length modulation. Assume that the current source requires a minimum voltage of to operate properly. (a) Find and for each transistor. (b) For , find , and . (c) Repeat (B) for . (d) Repeat (b) for . (e) What is the highest permitted value of ? (f) What is the lowest value allowed for ?