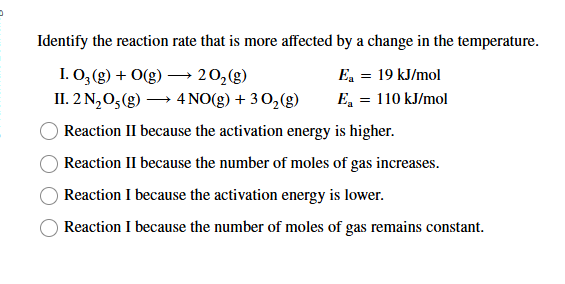Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
identify-the-reaction-rate-that-is-more-affected-by-a-change-in-the-temperature-i-o-3-g-o-g-lon-pa867
(Solved): Identify the reaction rate that is more affected by a change in the temperature. I. O_(3)(g)+O(g)lon ...
Identify the reaction rate that is more affected by a change in the temperature.
I. O_(3)(g)+O(g)longrightarrow2O_(2)(g)
E_(a)=19k(J)/(m)ol
II. 2N_(2)O_(5)(g)longrightarrow4NO(g)+3O_(2)(g)
E_(a )=110k(J)/(m)ol
Reaction II because the activation energy is higher.
Reaction II because the number of moles of gas increases.
Reaction I because the activation energy is lower.
Reaction I because the number of moles of gas remains constant.