(Solved): PLEASE EXPLAIN STEP BY STEP Figure 1 shows the control scheme implemented by a pharmaceutical labor ...
PLEASE EXPLAIN STEP BY STEP
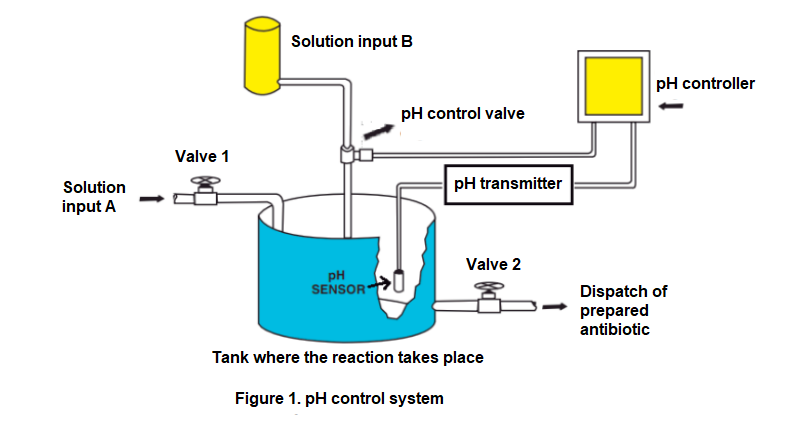
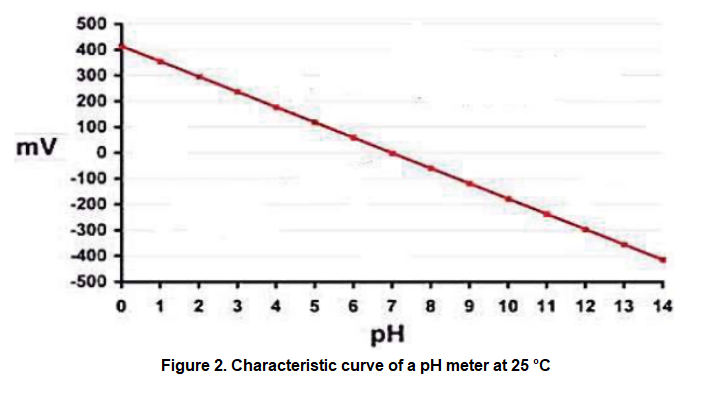
Figure 1 shows the control scheme implemented by a pharmaceutical laboratory to control the pH level of an antibiotic and keep it at a value of 8. The pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity level of an aqueous solution and is usually measure at a reference temperature of 25 °C, for which it is sought to have the laboratory room under said environmental conditions when making measurements of said variable. It is important to remember that decreasing the pH value increases the acidity of a substance. The pH level in the tank is measured using a phmeter, which is a device that generates a direct voltage level, linearly related to the pH level as shown in figure 2. Said voltage level is processed by a transmitter that sends a 4 mA to 20 mA current signal to the controller.
According to figure 1, two substances enter the tank: A solution A and a solution B. Solution A is a substance known as base and the amount of said substance added to the tank can vary depending on its availability and also due to the demand for production of the antibiotic. To vary the amount of solution A, the manual opening valve 1 is used. On the other hand, by regulating the amount of substance B (an acid) the pH level of the antibiotic in the tank is controlled, so if more of this solution were added to the tank, the pH of the antibiotic would decrease. The outlet valve opening is usually constant, however, it could be varied (using the manual opening valve 2) depending on the antibiotic production demand.
a.) Draw a block diagram of the process and its control system, describing all the physical variables and signals involved in it. Indicate and describe two variables that can be considered disturbances of the control system.
Expert Answer
The shapes of graph are frequently linear by the max