Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
question-6-the-element-in-figure7-is-fixed-at-point-b-has-a-comer-at-point-c-and-a-free-end-at-poi-pa500
(Solved): Question 6 The element in figure7 is fixed at point B, has a comer at point C, and a free end at poi ...
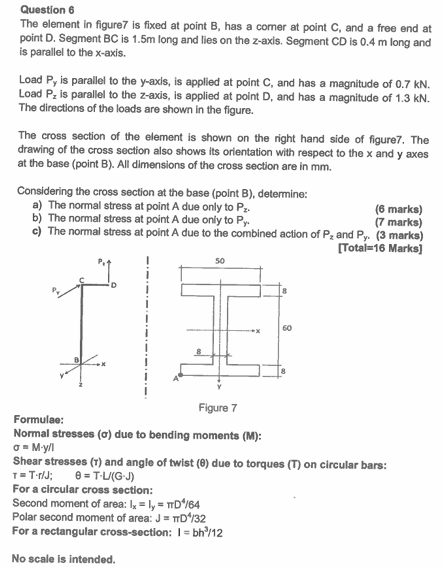
Question 6
The element in figure7 is fixed at point B, has a comer at point C, and a free end at
point D . Segment BC is 1.5 m long and lies on the z-axis. Segment CD is 0.4 m long and
is parallel to the x-axis.
Load P_(y) is parallel to the y -axis, is applied at point C , and has a magnitude of 0.7 kN .
Load P_(z) is parallel to the z-axis, is applied at point D, and has a magnitude of 1.3 kN .
The directions of the loads are shown in the figure.
The cross section of the element is shown on the right hand side of figure7. The
drawing of the cross section also shows its orientation with respect to the x and y axes
at the base (point B). All dimensions of the cross section are in mm.
Considering the cross section at the base (point B ), determine:
aA due only to P_(x).
bA due only to P_(y).
cA due to the combined action of P_(z) and P_(y). (3 marks)
[Total=16 Marks]
Formulas:
Normal stresses (\sigma ) due to bending moments (M) :
\sigma -=M*(y)/(l)\theta T=T*(r)/(J);,\theta =T*(L)/(G*J)
For a circular cross section:
Second moment of area: l_(x)=l_(y)=\pi (D^(4))/(64)
Polar second moment of area: J=\pi (D^(4))/(32)
For a rectangular cross-section: I=b(h^(3))/(12)
No scale is intended.