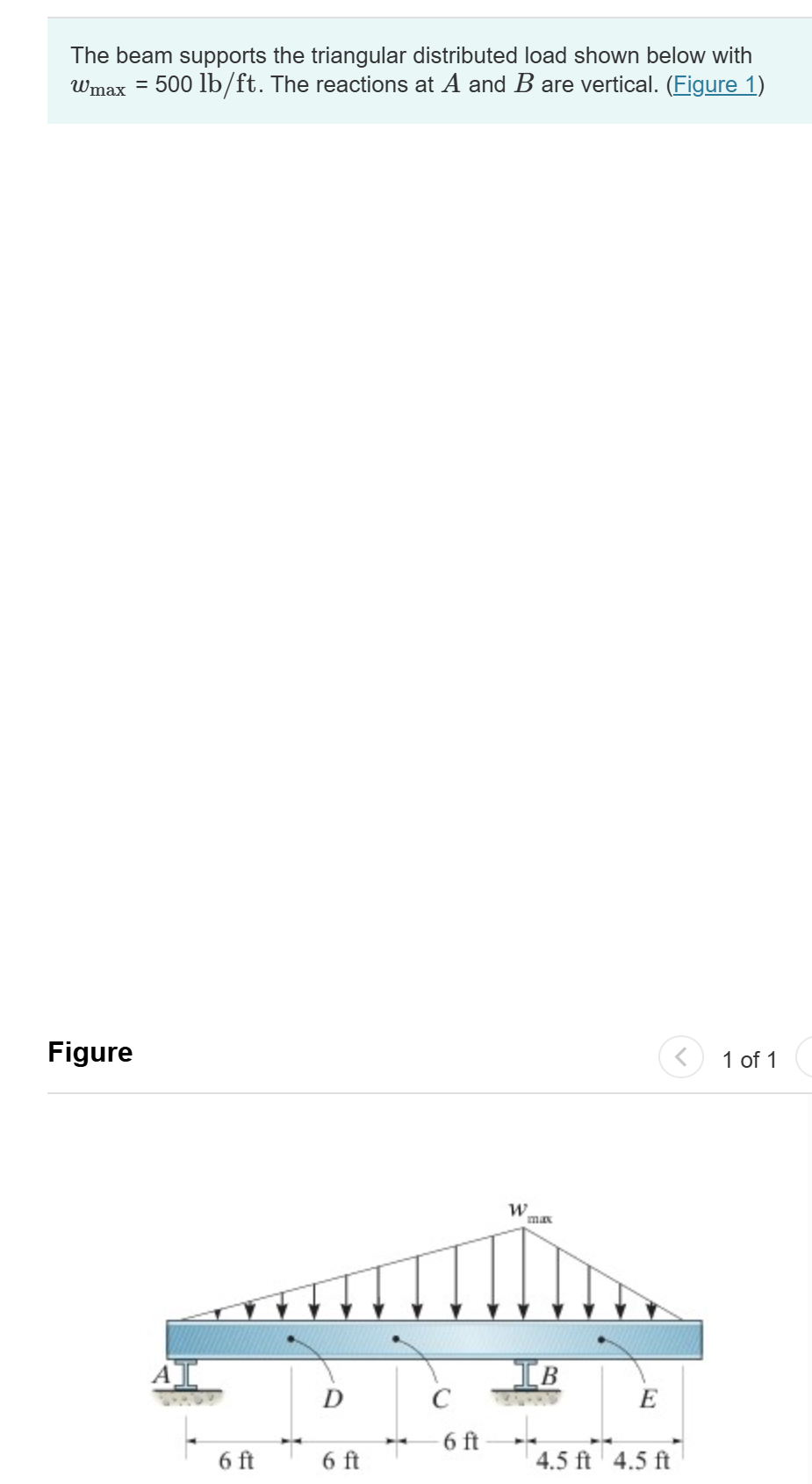
(Solved): The beam supports the triangular distributed load shown below with wmax = 500 lb/ft . The reaction ...
The beam supports the triangular distributed load shown below with wmax = 500 lb/ft . The reactions at A and B are vertical. (Figure 1) The beam supports the triangular distributed load shown below with
w_(max)=500l(b)/(f)t. The reactions at
Aand
Bare vertical. (Figure 1) Part A: Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal normal force on the cross section at point D. Express your answer in kilopounds to three significant figures. Part B: Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal shear force on the cross section at point D. Express your answer in kilopounds to three significant figures. Part C: Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal bending moment on the cross section at point D.Express your answer in kilopound-feet to three significant figures. Part D: Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal normal force on the cross section at point E.Express your answer in kilopounds to three significant figures. Part E: Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal shear force on the cross section at point E.Express your answer in kilopounds to three significant figures. Part F: Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal bending moment on the cross section at point E. Express your answer in kilopound-feet to three significant figures.