Home /
Expert Answers /
Computer Science /
using-c-data-structures-c-stl-inputs-and-expected-outputs-are-shown-below-lru-cache-lru-pa294
(Solved): Using C++, data structures, C++ STL, inputs and expected outputs are shown below. LRU Cache. LRU ...
Using C++, data structures, C++ STL, inputs and expected outputs are shown below. LRU Cache.
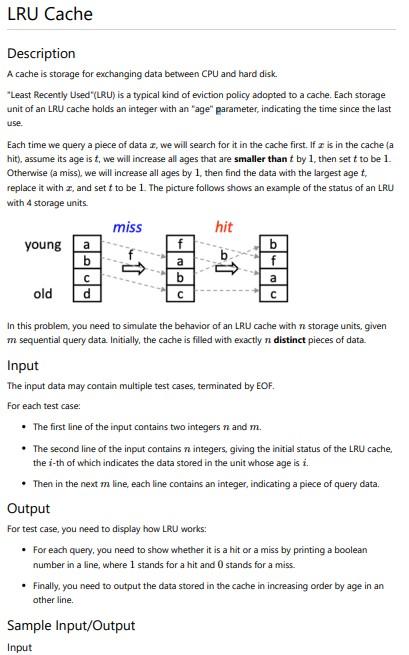
LRU Cache Description A cache is storage for exchanging data between CPU and hard disk. "Least Recently Used" (LRU) is a typical kind of eviction policy adopted to a cache. Each storage unit of an LRU cache holds an integer with an "age" parameter, indicating the time since the last use. Each time we query a piece of data , we will search for it in the cache first. If I is in the cache (a hit), assume its age ist, we will increase all ages that are smaller than t by 1, then sett to be 1. Otherwise (a miss), we will increase all ages by 1, then find the data with the largest aget, replace it with 2and set t to be 1. The picture follows shows an example of the status of an LRU with 4 storage units. miss hit young f b b f ? b a d a a old In this problem, you need to simulate the behavior of an LRU cache with n storage units, given m sequential query data. Initially, the cache is filled with exactly n distinct pieces of data. Input The input data may contain multiple test cases, terminated by EOF. For each test case . The first line of the input contains two integers n and m. • The second line of the input contains n integers, giving the initial status of the LRU cache, the i-th of which indicates the data stored in the unit whose age is i.. • Then in the next m line, each line contains an integer, indicating a piece of query data, Output For test case, you need to display how LRU works: . For each query, you need to show whether it is a hit or a miss by printing a boolean number in a line, where I stands for a hit and stands for a miss. . Finally, you need to output the data stored in the cache in increasing order by age in an other line. Sample Input/Output Input
44 1 2 3 4 5 4 2 1 12 2 1 1 Output 8811 1245 81 1 Constraint in < 104,1
Expert Answer
PROGRAM1: #include #include using namespace std; //Create Global variable for cache size(total number of cache lines) int cacheSize; //Create Global data structures for cache and TLB lookup on heap //Cache -> Queue list